Category AMS strategy

Appendicitis and antibiotics unpacked
Guest posting: Dr Celia Cooper, Paediatric Infectious Diseases & Microbiology, South Australia Pathology, Adelaide Dr Cooper’s recent presentation to the Australian New Zealand Paediatric Infectious Diseases Interest Group in November is provided with her permission. Her presentation highlights important messages: Post-operative antibiotics for patients with non-perforated appendicitis who have acute surgery are unnecessary (refer to IDSA Guidelines […]
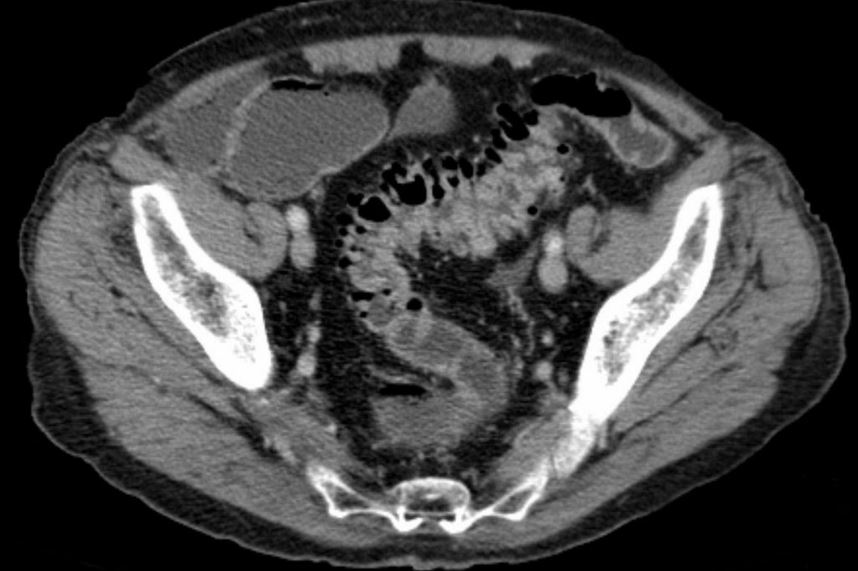
Let’s stop using antibiotics for uncomplicated diverticulitis
Guest posting : Dr Daniel Isacson, local GP (ex Swedish researcher) The evidence is out and there is no proven benefit in recovery or complication rates in treating these patients with or without antibiotics, but still many GPs and surgeons prefer to use antibiotics. How do we get the word across?

The art of antibiotic prescribing in general practice
Guest posting from Dr Gillian Deakin, General Practitioner and author of 101 Things Your GP Would Tell You If Only There Was Time. Beyond the usual medical challenges of appropriate prescribing, GPs also need skills to ensure that the patient accepts the treatment. Unlike the hospital patient where the patient is largely obliged to accept […]
Alternative recommended antibiotics to ceftriaxone by syndrome and bug
Ceftriaxone (a third generation cephalosporin-TGC) remains an overused agent in some of our (HNELHD) facilities. We aim to keep usage below 20 defined daily doses per 1000 patient-days (as is done at John Hunter Hospital for instance) to prevent adverse ecological impacts on resistance – increases in MRSA, VRE, multi-resistant Gram negatives and C. difficile are all associated […]
Reducing ESBL Gram negative fluoroquinolone resistance – what is the ecological sweet spot for usage?
This excellent recent paper from Sarma et al brings focus on what the target level of quinolone use should be in order to have an impact on quinolone resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. It describes the situation across a region of England (9 hospitals and other facilities) where quite stringent control of cephalosporin use was already in place […]
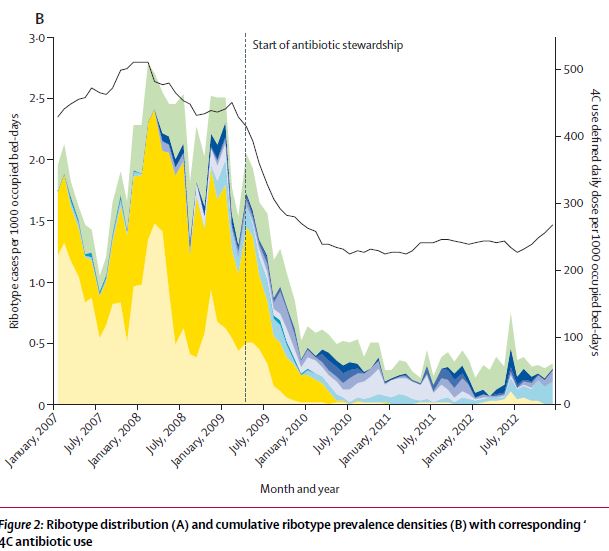
Inducing ceftriaxone-deficiency in hospitals: practical stewardship insights
2018 update! Just as relevant. Upside – Ceftriaxone and cefotaxime (third generation cephalosporins-TGC) are amongst the most important agents for directed therapy of infections due to Gram negative organisms that are resistant to ampicillin or cephazolin (a first generation cephalosporin), including Klebsiella pneumoniae . They penetrate the CSF well, making them important agents for treatment of meningitis due to […]
Aids to structuring antimicrobial stewardship rounds and improving documentation
We’ve used the following aids at John Hunter Hospital for some years which others are very welcome to adopt/adapt:
Choosing wisely (IDSA): Avoid antibiotic therapy for lower limb stasis dermatitis or venous ulcers
The Infectious Diseases Society of America also has started a Choosing wisely campaign. This advice is valuable. In the recent District-wide wound surveillance survey across Hunter New England Health hospitals and community nursing services, there were over 900 patients with active wounds identified (including many venous ulcers related to stasis dermatitis). Of these 28% had received antibiotics in […]
An everyday tragedy: treating asymptomatic bacteruria with antibiotics
Act 1 of a common tragedy that sets the scene for antibiotic resistance – an elderly female resident of a nursing home complains of minor dysuria or perhaps just has urine that appears cloudy or smelly. The nurse collects some urine and performs a urinalysis that shows presence of white cells and nitrite. The urine is sent […]
Australia releases first National Strategy to address Antimicrobial Resistance
This week Health Minister, Susan Ley and Agriculture Minister, Barnaby Joyce released a statement regarding the publication of Australia’s first national strategy to address antimicrobial resistance. The strategy covers the next 4 years and aims to reduce Australia’s antimicrobial use to combat resistance. It is based on the WHO Global Action Plan for AMR. The […]