Category Antimicrobial

Is it cellulitis? The case of itchy red legs
66 year old woman with 12 month history of itchy red legs. She dated the start of the problem from an excision of a skin lesion from the left shin. She notes persistent redness occurring over both lower legs, more marked on the left side, and this has been associated with marked itchiness after showering. […]

Extrapolating antibiotic susceptibility for streptococci including the pneumococcus
This posting concerns betahaemolytic species of streptococci including S. pyogenes (Lancefield group A strep), S. agalactiae ((group B strep), S. dysgalactiae group (betahaemolytic large colony, groups C or G) (several species included) which are usually associated with pyogenic infection, especially of skin and soft tissue. S. pneumoniae (the pneumococcus ) is also considered. A key misunderstanding about […]

Sparing fluoroquinolones – alternative safe and effective options by syndrome and bug
Fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and moxifloxacin) have serious potential side effects, and are best used only for directed therapy of serious multi-resistant Gram negative infections where no other safer alternatives are available. 14 of our 32 hospital facilities in HNELHD overuse these agents with 2016 average FQ usage above our current benchmark of 30 defined daily doses per 1000 patient-days. […]

Ciprofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones: should you think twice about prescribing?
Fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin and norfloxacin) (FQ) are essential agents for directed treatment of certain types of resistant aerobic Gram negative bacterial species where FQ susceptibility has been proven. They are best avoided as empirical therapy or where there is an alternative due to these potential serious side effects:
Sparing meropenem 101: what alternatives exist for the treatment of ESBL-producers?
Guest post: Patrick Harris, Staff Specialist in Microbiology, Central Laboratory, Pathology Queensland, Brisbane In a previous post we looked at bacteria that produce AmpC-type beta-lactamases, such as Enterobacter spp. Perhaps a more familiar, and increasingly common, problem is presented by species such as E. coli or K. pneumoniae, which have acquired extended-spectrum beta-lactamase enzymes (or ‘ESBLs’). […]

Antibiotics and the QT Interval
Guest post : Ian Whyte, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology at Calvary Mater Newcastle and University of Newcastle Case report (Knorr et al 2008 Ciprofloxacin-induced Q-T interval prolongation) 16-year-old boy was admitted for the treatment of an acute flare of Crohn’s disease and a perirectal abscess. The patient was started on ciprofloxacin 400 mg IV twice daily […]
Alternative recommended antibiotics to ceftriaxone by syndrome and bug
Ceftriaxone (a third generation cephalosporin-TGC) remains an overused agent in some of our (HNELHD) facilities. We aim to keep usage below 20 defined daily doses per 1000 patient-days (as is done at John Hunter Hospital for instance) to prevent adverse ecological impacts on resistance – increases in MRSA, VRE, multi-resistant Gram negatives and C. difficile are all associated […]

Vitamin ‘C1’ – cefazolin, cephalexin and cephalothin unpacked
These so-called first generation cephalosporins (C1) remain important agents for skin, soft tissue and urinary tract infections due to susceptible organisms and for surgical prophylaxis. Increases in community acquired MRSA in some regions may lead to a different empiric choice for skin/soft tissue infection (e.g. doxycycline or trimethoprim+sulphamethoxazole). Local cumulative antibiograms should also be examined to […]
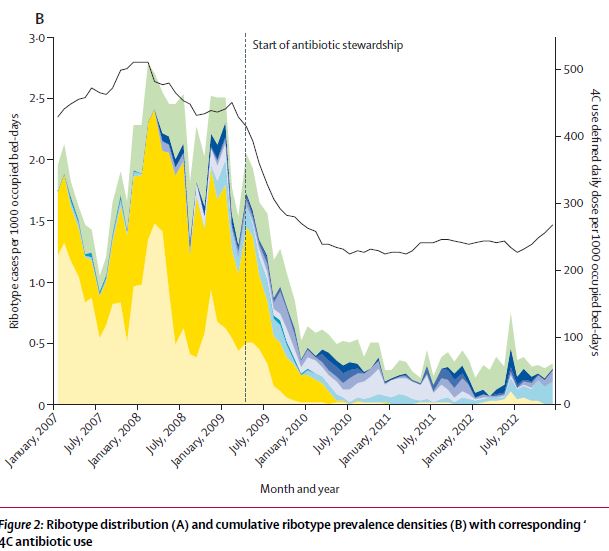
Inducing ceftriaxone-deficiency in hospitals: practical stewardship insights
2018 update! Just as relevant. Upside – Ceftriaxone and cefotaxime (third generation cephalosporins-TGC) are amongst the most important agents for directed therapy of infections due to Gram negative organisms that are resistant to ampicillin or cephazolin (a first generation cephalosporin), including Klebsiella pneumoniae . They penetrate the CSF well, making them important agents for treatment of meningitis due to […]
