Category Respiratory

Why does our local CAP guideline differ from Australian Therapeutic Guidelines?
Kristi, Lorrae and Ayesha have recently joined as AIMED authors– welcome aboard. Here’s a posting from Kristi that unpacks the approach to community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in Hunter New England Health, NSW. In adults, the most common bacterial cause of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is Streptococcus pneumoniae. Other pathogens associated with CAP include Haemophilus influenzae and atypical’ […]

Do we need to cover ‘atypical’ community acquired pneumonia?
Guest posting: Dr John Burston, Staff Specialist, Infectious Diseases, Calvary Mater Hospital, Newcastle. Most antibiotic guidelines1-3 , including the HNELHD Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) guideline, suggest empirically treating community acquired pneumonia (CAP) with a macrolide or tetracycline to cover ‘atypical’ organisms. But is this necessary and what should be our approach? Beta-lactam monotherapy was non-inferior […]

Acute sinusitis and sore throat in primary care – what evidence?
An excellent paper by Professor Chris Del Mar in Australian Prescriber unpacks the Cochrane reviews on the (quite minimal) value of antimicrobial treatment of these conditions. The evidence level is quite robust. For a summary, see below. It couples nicely with a recent pragmatic randomized controlled trial that examined the effectiveness of steam inhalation and nasal irrigation […]

Extrapolating antibiotic susceptibility for streptococci including the pneumococcus
This posting concerns betahaemolytic species of streptococci including S. pyogenes (Lancefield group A strep), S. agalactiae ((group B strep), S. dysgalactiae group (betahaemolytic large colony, groups C or G) (several species included) which are usually associated with pyogenic infection, especially of skin and soft tissue. S. pneumoniae (the pneumococcus ) is also considered. A key misunderstanding about […]

Pertussis questions from one of our general practitioners
An 8 year old child with a history of cough for 2 weeks +. The GP tested the child by throat swab and PCR which was positive. A 7 day course of erythromycin was prescribed. Reviewed then and patient complaining that the cough worsening. Q & A : The cough is worsening – does he […]

Is penicillin enough for aspiration pneumonia?
There has been quite a tradition for including Gram negative anaerobic cover for patients suspected to have aspiration pneumonia. There are virtually no randomised trials that directly address the issue with nearly all such trials including agents that have Gram negative anaerobic cover across all treatment arms. One exception was a small trial from 1997 in a paediatric […]
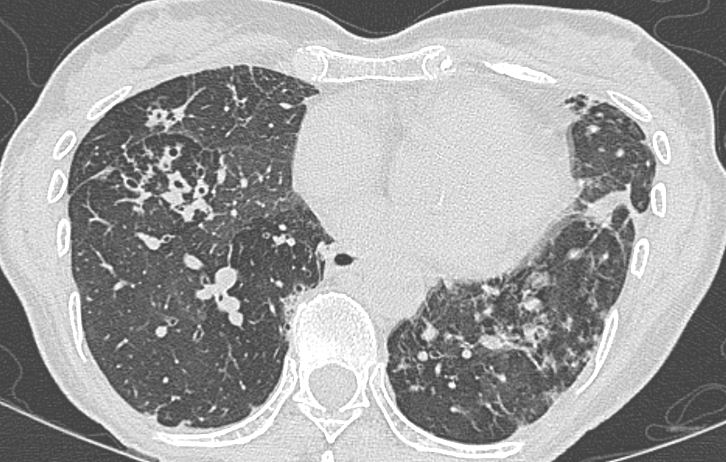
Bronchiectasis and goals of antibiotic treatment – thinking it through
The setting – patients with bronchiectasis (including those with cystic fibrosis) have impaired respiratory secretion clearance and a vastly different lower respiratory flora (microbiome) than patients with normal lungs. They are frequently colonised with conventional respiratory species such as Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis, Staphylococcus aureus, a diverse range of Gram negative bacteria and even fungi. Colonisation/infection with non-tuberculous […]
Tazocin misconceptions: misuse in community-acquired pneumonia – spectrum too broad
Piperacillin+tazobactam (Tazocin) is an important broad spectrum antibiotic that is still active in most Australian settings against a wide range of Gram negatives (including Pseudomonas) , Gram positives (excluding MRSA and VRE) and nearly all anaerobic bacteria. It comes into great demand for management of a range of healthcare-associated infections, especially in ICU. Its use […]
