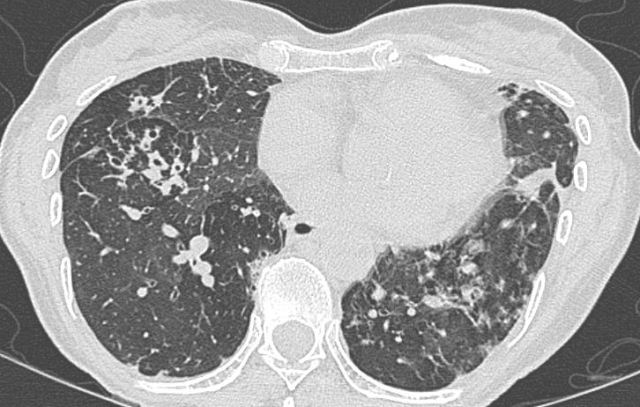
The setting – patients with bronchiectasis (including those with cystic fibrosis) have impaired respiratory secretion clearance and a vastly different lower respiratory flora (microbiome) than patients with normal lungs. They are frequently colonised with conventional respiratory species such as Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis, Staphylococcus aureus, a diverse range of Gram negative bacteria and even fungi. Colonisation/infection with non-tuberculous […]
2018 update! Just as relevant. Upside – Ceftriaxone and cefotaxime (third generation cephalosporins-TGC) are amongst the most important agents for directed therapy of infections due to Gram negative organisms that are resistant to ampicillin or cephazolin (a first generation cephalosporin), including Klebsiella pneumoniae . They penetrate the CSF well, making them important agents for treatment of meningitis due to […]
The terms Gram positive and Gram negative are commonly used to describe bacteria. The main difference between the two is the structure of their cell wall which changes their susceptibility to different antibiotics. The separation also loosely fits the location of these organisms in the body – Gram negative organisms predominate in the bowel (eg. […]
Piperacillin+tazobactam (Tazocin) is an important broad spectrum antibiotic that is still active in most Australian settings against a wide range of Gram negatives (including Pseudomonas) , Gram positives (excluding MRSA and VRE) and nearly all anaerobic bacteria. It comes into great demand for management of a range of healthcare-associated infections, especially in ICU. Its use […]
We’ve used the following aids at John Hunter Hospital for some years which others are very welcome to adopt/adapt:
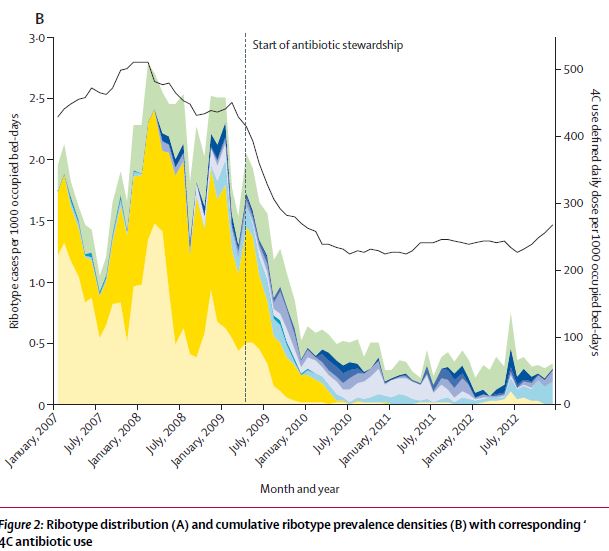
In northern NSW, we already face cases similar to that described below – infection with multi-drug resistant carbapenemase-producing Gram negative organisms. The major global types of these organisms are named with acronyms that refer to the type of carbapenemase gene – KPC, NDM (New Delhi Metallobetalactamase), IMP (imipenemase) and others. KPC-type organisms are prevalent in Greece, […]
The Infectious Diseases Society of America also has started a Choosing wisely campaign. This advice is valuable. In the recent District-wide wound surveillance survey across Hunter New England Health hospitals and community nursing services, there were over 900 patients with active wounds identified (including many venous ulcers related to stasis dermatitis). Of these 28% had received antibiotics in […]
Act 1 of a common tragedy that sets the scene for antibiotic resistance – an elderly female resident of a nursing home complains of minor dysuria or perhaps just has urine that appears cloudy or smelly. The nurse collects some urine and performs a urinalysis that shows presence of white cells and nitrite. The urine is sent […]
Thanks Craig Boutlis who helped me develop these some time back. Nothing has changed much yet! Always disinfect your hands with alcohol-based hand rub BEFORE and AFTER touching a patient or performing a procedure. Set the example for your team and expect others to follow your lead. Dress well for safer care – abandon ties […]
Diagnostic error is a major factor leading to inappropriate antimicrobial use- recent landmark paper
Diagnostic accuracy is a factor neglected by most antimicrobial stewardship programs and should perhaps be subject to regular audit and feedback. It is heavily dependent upon the context of the clinical contact – for example, time-pressured, after hours hospital ward patient encounters are prone to quick judgements and sloppy diagnoses. For a persuasive discussion of […]