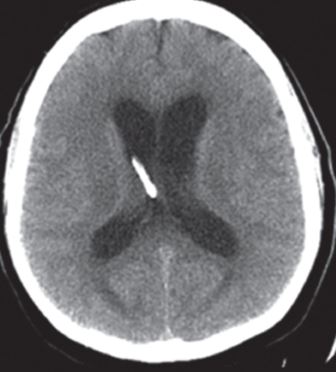
Guest posting : Dr Jonathan Ash, Advanced training registrar, John Hunter Hospital. Ventriculitis is a rare but potentially disastrous complication of external ventricular drain placement, and with increasing rates of multi-drug resistant organisms, effective parenteral antibiotic choices are limited. Colistin has an established role in the treatment of infections caused by MDR Gram negatives, particularly […]

SITUATION Due to a global shortage, many Hunter New England Local Health District sites have low supplies of piperacillin+tazobactam with shortages likely until after September. It is essential that further use of this agent is conserved as below. Amoxycillin+clavulanate is now available in a parenteral form and is a suitable option in many circumstances, contingent on local […]

An article in The Medical Observer by Dr. Sergio Diez Alvarez of the University of Newcastle comments on alarming trends of antibiotic resistance, the current problems with antibiotic stewardship and potential strategies to improve on reducing resistance. Whilst Dr Alvarez’s article provides some excellent comments for reflection on antibiotic use in humans, it is his discussion regarding […]

Piperacillin+tazobactam (Tazocin) is one of our most important broad spectrum agents and is in short supply. Please conserve it by avoiding use in these common situations: Uncomplicated biliary sepsis (Use ampicillin+gentamicin(max 48hrs) OR if allergic, ceftriaxone) Urinary tract infection with sepsis (Use ampicillin+gentamicin(max 48 hrs) OR if allergic, ceftriaxone) Early onset (< 5d after admission) […]

We’ve previously counselled against augmentin overuse in a number of conditions which did not, however, include intra-abdominal infection where the new availability of an IV preparation offers us a way of reducing the use of the workhorse antibiotic piperacillin+tazobactam. Here is our freshly minted guideline which also provides more explicit advice about short or no […]
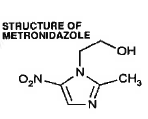
Guest post: Dr Rod Givney, Pathology North Microbiologist. How well do you know these commonly used drugs, their pros and cons? Here is an up-to-date overview prepared for our advanced trainee tutorial series. Nitroimidazoles overview 2017 Givney.

Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection (septicaemia) information card [Patient Label ] [ [ You were recently diagnosed with a blood infection caused by a bacterium called Staphylococcus aureus (“Golden Staph”). This infection has been treated with intravenous antibiotics. Whilst this usually cures the infection, there is a possibility that your infection could return within 3 months […]

The Special Access Scheme (SAS) allows practitioners to import/gain access to therapeutic goods currently not registered on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG) for a single patient on a case by case basis. Fosfomycin (one such SAS drug) is a broad spectrum antibiotic belonging to the phosphonic acid derivative drug class (other examples in this drug class include foscarnet and adefovir).
At the bottom of each article click the “Print & PDF” tab under the “Share this” heading next to the social media tabs (see below). This should link you to a version of the article that is print-friendly.

Eradication treatment aims to remove Staph. aureus (MRSA or MSSA) and reduce your risk from recurrent skin infection. If the first eradication treatment is unsuccessful, repeat treatment may be required. MRSA= methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (commonly referred to as golden staph); MSSA = methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus